Avo Codegen in Objective-C
Platforms
Avo can code generate Avo Codegen in Objective-C for your iOS tracking.
Quickstart
Avo Codegen usage consists of 4 steps.
Step 1. Include the Avo file
Pull the generated code with the Avo CLI
To get the Avo generated Objective-C file you must be a member of an Avo workspace with an Objective-C source. Ask for an invite from a colleague or create a new workspace.
npm install -g avo
avo login
avo pull --branch my-branch-nameLearn more about the CLI here.
You can also download the file manually from your Avo workspace.
Step 2. Initialize Avo
Initialize Avo by creating an object using constructor from the generated Avo file
val avo = Avo(env: .dev/*, other parameters depending on your tracking plan setup*/)
[Avo initAvoWithEnv:AVOEnvDev
/*other parameters depending on your tracking plan setup*/];The actual parameters depend on your tracking plan setup, see the parameters explanation in the reference below.
Step 3. Call Avo Codegen to track your product usage
Every event in your tracking plan, marked with the “Implement with Codegen” checkbox, gets a function in the generated code, named according to the event name, in camelCase.
For example, if you have a “Signup Start” event defined like this in Avo:
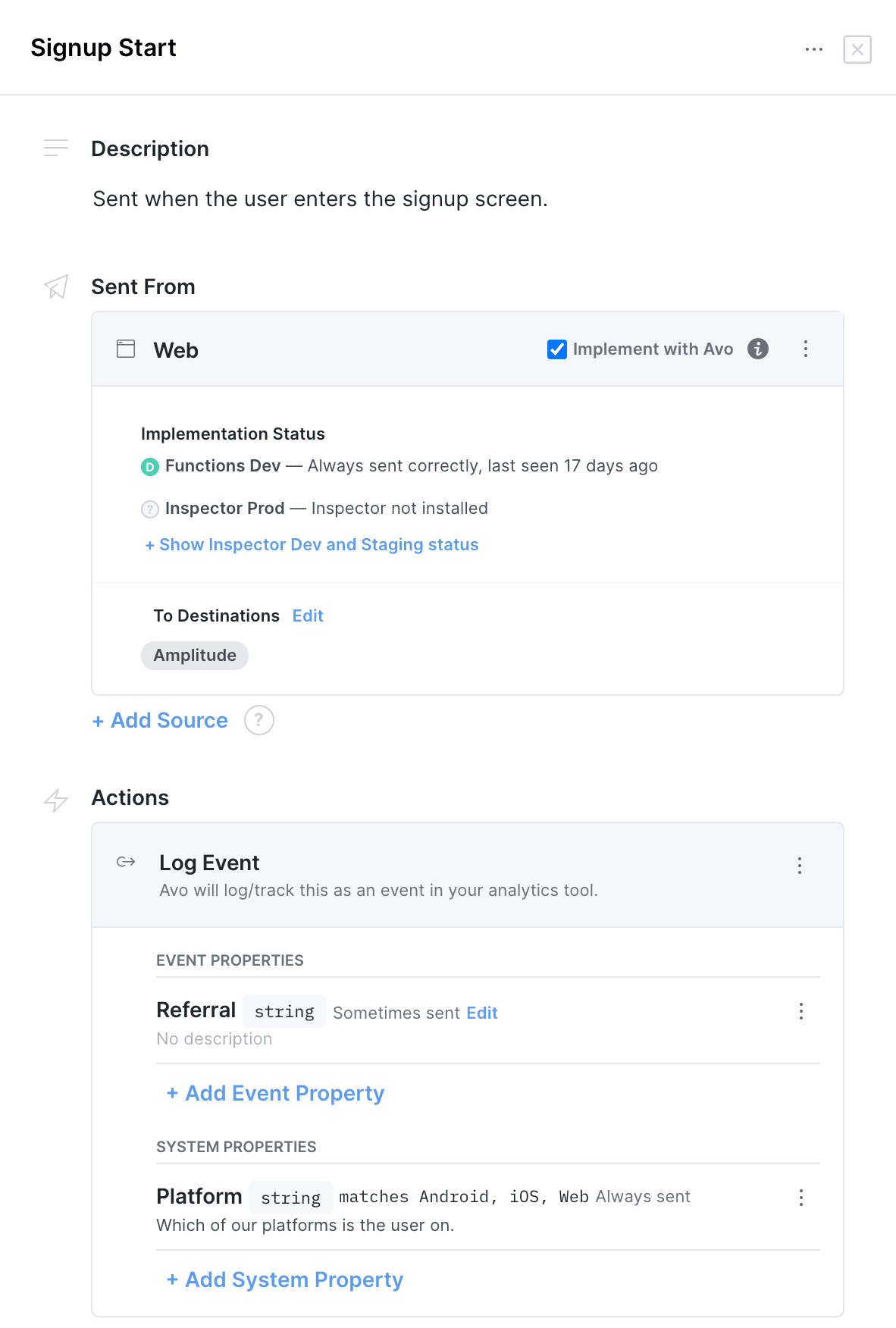
You’ll be able to call it like this from the generated code
[Avo signupStartWithReferral:@"direct"];Notice, that you are not passing the System property with the call. System properties are defined on the init step and then automatically included with all events. You can update the system properties with
setSystemProperties...function.
Step 4. Verify the implementation
Use the Implementation status in your Avo workspace and the Avo Inspector to verify that your implementation is correct. If you don’t want to use Avo Inspector you can use the standalone visual debugger.
Reference
Constructor
+ (void)initAvoWithEnv:(AVOEnv)env
// Other parameters may not be present, depending on your tracking plan
systemProperty0:(nullable NSNumber *)systemProperty0
systemProperty1:(BOOL)systemProperty1
mixpanelDestination:(nonnull id<AVOCustomDestination>)mixpanelDestination
segmentDestination:(nonnull id<AVOCustomDestination>)segmentDestination
otherDestination:(nonnull id<AVOCustomDestination>)otherDestination
strict:(BOOL)strict
noop:(BOOL)noop;This method will call the makeWithEnv:withApiKey: callback in all the provided destination interfaces. It will also initialize the analytics SDKs of the legacy Avo Managed destinations.
Arguments
(AVOEnv) env: Can be set to AVOEnvProd, AVOEnvDev.
systemProperties: a number of parameters equal to the number of system properties defined in your Avo workspace.
The parameters are named the same as system properties, in camelCase, and require corresponding types: string, int, long, float, bool or list.
(nonnull id<AVOCustomDestination>) destination: object, each destination you are sending events to gets a separate parameter in the init function with callbacks that the Avo generated code will trigger, unless you are using the legacy Avo managed destinations. Each method in the destination interface is directly mapped to the Actions attached to each event in Avo. Learn more about event Actions in this doc.
@protocol AVOCustomDestination
- (void)make:(AVOEnv)avoEnv;
- (void)logEvent:(nonnull NSString*)eventName withEventProperties:(nonnull NSDictionary*)eventProperties;
- (void)logPage:(nonnull NSString*)pageName withEventProperties:(nonnull NSDictionary*)eventProperties;
- (void)revenue:(double)amount withEventProperties:(nonnull NSDictionary*)eventProperties;
- (void)setUserProperties:(nonnull NSString*)userId withUserProperties:(nonnull NSDictionary*)userProperties;
- (void)identify:(nonnull NSString*)userId;
- (void)unidentify;
@end(BOOL) strict: bool, default value is true, if true, Avo will throw an exception when it detects a tracking problem in development or staging. Note that the strict flag is ignored in production.
(BOOL) noop: bool, default value is false, if true, Avo won’t make any network calls (no tracking) in development and staging environments. Note that the noop flag is ignored in production.
Note that you do not need to pass Avo Inspector instance to the constructor. It will be automatically picked up if you include the library and enable Avo Inspector for your iOS source in the Avo workspace. Read more here.
Destination interface example
@interface CustomDestination()
@property (nonatomic, readwrite) NSString* apiKey;
@end
// Example: Destination interface for the Mixpanel SDK. Replace the Mixpanel implementation with your own tracking SDK methods
@implementation CustomDestination : NSObject <AVOCustomDestination>
// This method is optional, you can skip it if you've already initialized your Analytics SDK
- (void)makeWithEnv:(AVOEnv)avoEnv withApiKey:(nonnull NSString*) apiKey
{
self.apiKey = apiKey;
}
- (void)logEvent:(nonnull NSString*)eventName withEventProperties:(nonnull NSDictionary*)eventProperties
{
[[Mixpanel sharedInstanceWithToken:self.apiKey] track:eventName properties:eventProperties];
}
- (void)logPage:(nonnull NSString*)pageName withEventProperties:(nonnull NSDictionary*)eventProperties
{
// Note: Mixpanel does not provide a native method for page or screen tracking, so we send an event instead. Other SDKs may have a dedicated page tracking method.
NSMutableDictionary *mutableEventProperties = [eventProperties mutableCopy];
mutableEventProperties[@"Page Name"] = pageName;
[[Mixpanel sharedInstanceWithToken:self.apiKey] track:"Page Viewed" properties:mutableEventProperties];
}
- (void)revenue:(double)amount withEventProperties:(nonnull NSDictionary*)eventProperties
{
[[[Mixpanel sharedInstanceWithToken:self.apiKey] people] trackCharge:amount withProperties:eventProperties];
}
- (void)setUserProperties:(nonnull NSString*)userId withUserProperties:(nonnull NSDictionary*)userProperties
{
[[[Mixpanel sharedInstanceWithToken:self.apiKey] people] set:userProperties];
}
- (void)identify:(nonnull NSString*)userId
{
[[Mixpanel sharedInstanceWithToken:self.apiKey] identify:userId];
}
- (void)unidentify
{
[[Mixpanel sharedInstanceWithToken:self.apiKey] reset];
}Read more about the destination interface here.
setSystemProperties
+ (void)setSystemPropertiesWithSystemProperty0:(NSInteger)systemProperty0
systemProperty1:(nullable NSNumber *)systemProperty1
...;A method to update system properties after initialization.
Arguments
systemProperties: a number of parameters equal to the number of system properties defined in your Avo workspace.
The parameters are named the same as system properties, in camelCase, and require corresponding types: string, int, long, float, bool or list.
Event tracking functions
+ (void)[yourEventName]WithEventProperty0:(NSInteger)eventProperty0
eventProperty1:(nullable NSNumber *)eventProperty1
userProperty0:(BOOL)userProperty0
userProperty1:(BOOL)userProperty1
userId:(nonnull NSString *)userId_
...];Every event you define in your tracking plan in Avo gets a function named after the event in camelCase. The arguments of the function depend on how it’s defined in your tracking plan
Arguments
eventProperty: type defined in the Avo tracking plan, can be string, int, long, float, bool or list:
Every event property attached to the event in the Avo UI gets a corresponding argument. The argument key is camelCase version of the property name.
Pass the value of the property to track here.
userProperty: type defined in the Avo tracking plan as a user property, can be string, int, long, float, bool or list:
Every user property attached to the event in the Avo UI gets a corresponding argument. The argument key is camelCase version of the property name.
Pass the value of the property to update here.
(nonnull NSString *) userId_:
Added if the event has the Identify User action
Destinations
You can send your data using the Avo generated Swift code to any data destination that accepts custom events, including:
- Amplitude
- FacebookAnalytics
- FullStory
- Mixpanel
- Mixpanel
- Permutive
- Segment
- Snowplow
- ZendeskConnect
- Adobe Analytics
- Apptelemetry
- RudderStack
- Freshpaint
- PostHog
- Google Analytics 4 / Firebase Analytics
- Heap
- Keen
- Kissmetrics
- LaunchDarkly Events
- Pendo
- Fivetran
- AppsFlyer
- Braze
- Intercom
- A home made SDK
- Internal API